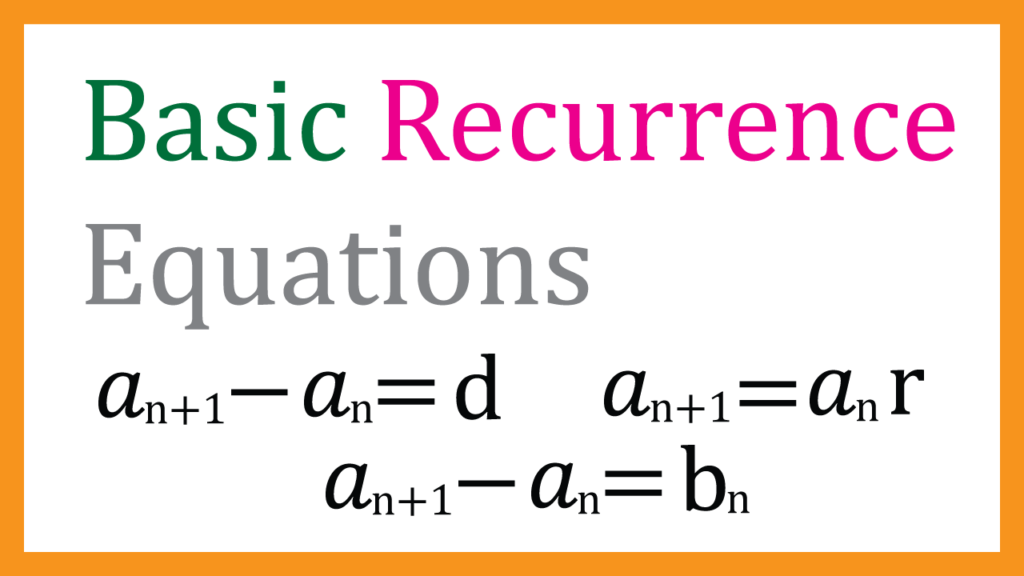
Basic 3 Patterns
Arithmetic Progression
$$a_{n+1}-a_n=d$$
This is the recurrence equation of Arithmetic Progression
Example Question
$$a_1=1,\ \ a_{n+1}-a_n=3 $$
If we write the sequence
$$1,\ 4,\ 7,\ 10,\ 13,\ 16,\ …$$
Formula for \(a_n\) of an arithmetic sequence is
$$a_n=a_1+(n-1)d$$
So \(a_n\) for this Example Question is
$$a_n= 1+(n-1)(3)$$
$$a_n=3n-2$$
In the question for the recurrence equation, only you get is
$$a_{n+1}-a_n=3$$
you need to imagine the sequence\({1,\ 4,\ 7,\ 10,\ 13,\ 16,\ …}\), then you have to use the formula of Arithmetic Progression to get the \(a_n\)
$$a_n=3n-2$$
Geometric Progression
The recurrence equation of a Geometric Progression is
$$a_{n+1}=a_n r$$
Example Question
$$a_1=1,\ \ a_{n+1}=2 a_n$$
We need to imagine that this sequence is like
$$1,\ 2,\ 4,\ 8,\ 16,\ 32,\ 64,\ …$$
Then use the formula of Geometric Equation to get the \(a_n\) of it
$$a_n=a_1 r^{n-1}$$
$$a_n=2^{n-1}$$
Differences Progression
$$a_{n+1}-a_n=b_n$$
Example Question
$$a_1=6,\ a_{n+1}-a_n=2n+3$$
If you see \(a_{n+1}-a_n=b_n\), it is differences progression
Since
$$b_n=2n+3$$
$${b_n}=5,\ 7,\ 9,\ 11,\ 13,\ …$$
Use the formula for \(a_n\) of a differences progression
$$a_n=a_1+\sum^{n-1}_{k=1} b_k \ (n≧2)$$
when \(n=1, a_n=a_1\)
$$a_n=6 +
\sum^{n-1}_{k=1} (2k+3) $$
$$=6+2\bigg( \frac{(n-1)n}{2}\bigg)+ 3(n-1)$$
Remember
$$\sum^{n}_{k=1} k=\frac{n(n+1)}{2}$$
$$\sum^{n}_{k=1} 3=3n $$
$$=6+(n-1)n+3(n-1)$$
$$=n^2+2n+3$$
Since when \( n=1,\ a_1= 6\)
$$a_n=n^2+2n+3 $$

コメント